Schizophrenia is an incurable, yet manageable chronic mental health condition that affects an individual’s ability to think, feel, and behave clearly. According to research, more than 21 million individuals worldwide are diagnosed with schizophrenia, and it is estimated that half of these individuals suffer from a co-occurring disorder. Additionally, research has discovered numerous links between schizophrenia and addiction.
This co-occurrence has been debated heavily for a number of years. To explain, most researchers believe that substances such as alcohol or drugs do not cause schizophrenia, rather individuals with this mental disorder begin to abuse substances in order to self-medicate. However, some researchers have indicated that certain substances can increase the risk of developing schizophrenia.
This particular type of psychosis known as schizophrenia has many overlapping symptoms as with addiction. As a result, these disorders are sometimes difficult to diagnose. Similarly, they pose additional challenges to individuals in recovery. Fortunately, many treatment centers incorporate the recovery of co-occurring disorders such as schizophrenia and addiction into their treatment modalities. In other words, individuals with these conditions should seek professional help such as dual diagnosis treatment.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition that causes individuals to experience delusional or irrational thinking. Medically, schizophrenia is described as a form of psychosis because this condition causes people to be unable to distinguish their thoughts and ideas from reality. Additionally, individuals with schizophrenia may display signs of paranoia and psychosis where they hear voices in their heads or see things that do not exist.
Individuals with schizophrenia may also suffer from drastic changes in behavior, becoming upset, anxious, confused, angry, or suspicious in short periods of time. Unfortunately, many individuals with schizophrenia do not believe that they need help causing them to seek out forms of self-medication such as abusing substances.
Similar to addiction, schizophrenia may occur despite a person’s race, age, gender, social status, or family history. However, schizophrenia is slightly more common in males than females, and the onset of this condition is more prevalent in adolescent years or early adulthood. When schizophrenia is active, an individual will not think or behave in a functional manner. This disease typically develops slowly and begins during the teenage years. As a result, this condition is difficult to identify due to the similarity between the symptoms of schizophrenia and common adolescent behaviors.
Symptoms of Schizophrenia
The symptoms of schizophrenia may vary from person to person by severity, frequency, and duration. However, there are common signs of schizophrenia that can make spotting this mental health condition easier. For example, some symptoms of this condition include not taking medications as prescribed, abusing drugs or alcohol, and high levels of stress.
Additionally, some of the common symptoms of schizophrenia include:
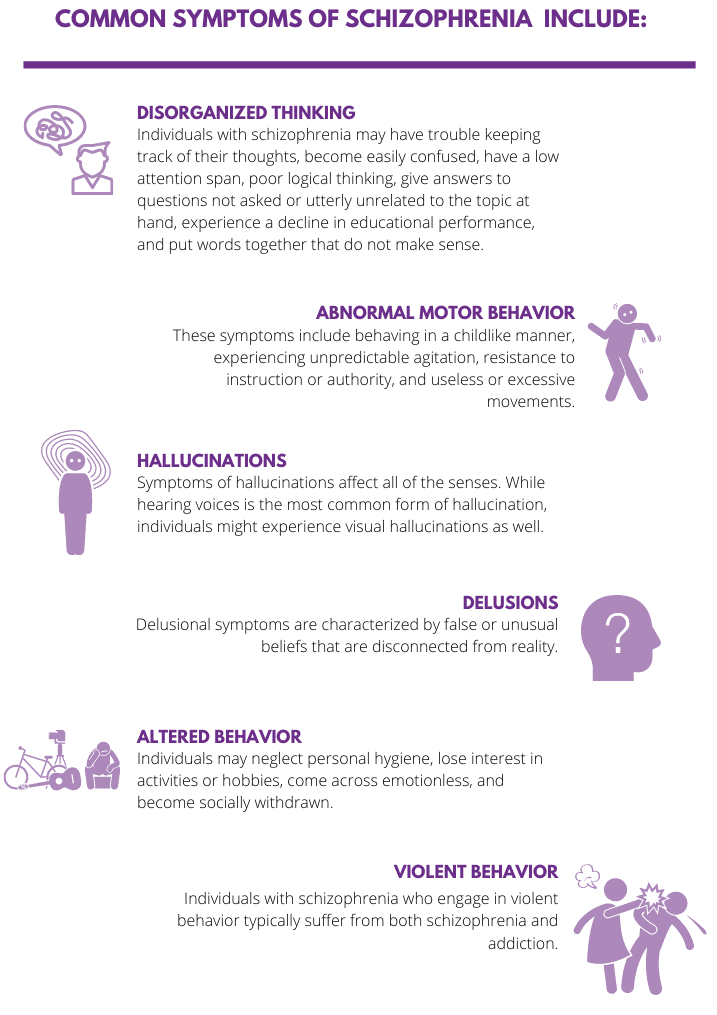
How do Schizophrenia and Addiction Relate?
Schizophrenia and addiction are common co-occurring disorders. In fact, individuals with schizophrenia are 4.6 times more likely to be diagnosed with a substance use disorder than the general population. To explain, the co-occurrence of schizophrenia and addiction most often occurs with the mental condition developing first, causing individuals to self-medicate with alcohol or drugs. As a result of drug or alcohol abuse, individuals with schizophrenia will experience exacerbated symptoms.
Individuals with schizophrenia most commonly abuse alcohol, nicotine, cocaine, and marijuana. Abusing these substances causes individuals with schizophrenia to experience more cognitive impairment, more intense psychosis, and higher rates of needing emergency services. Unfortunately, the worsening of symptoms can lead an individual to self-medicate even further, causing the development of alcohol or drug dependency and addiction. However, individuals with schizophrenia and addiction have the ability to recover through attending a dual-diagnosis treatment center. If you or a loved one are suffering from the co-occurrence of schizophrenia and addiction, now is the time to seek help.
Dual Diagnosis Treatment for Schizophrenia and Addiction
According to research conducted in 2014, 7.9 million people in the U.S. experience a mental disorder and substance use disorder simultaneously. Co-occurring disorders are best treated with an integrative approach that incorporates addiction and mental health treatment simultaneously.
If you or a loved one are suffering from co-occurring disorders such as schizophrenia and addiction, attending a dual diagnosis treatment center is vital for your recovery. Contact Agape Treatment Center today for more information on our comprehensive and individualized dual diagnosis treatment program.







